Apache vs LiteSpeed: Which Web Server is Right for You?
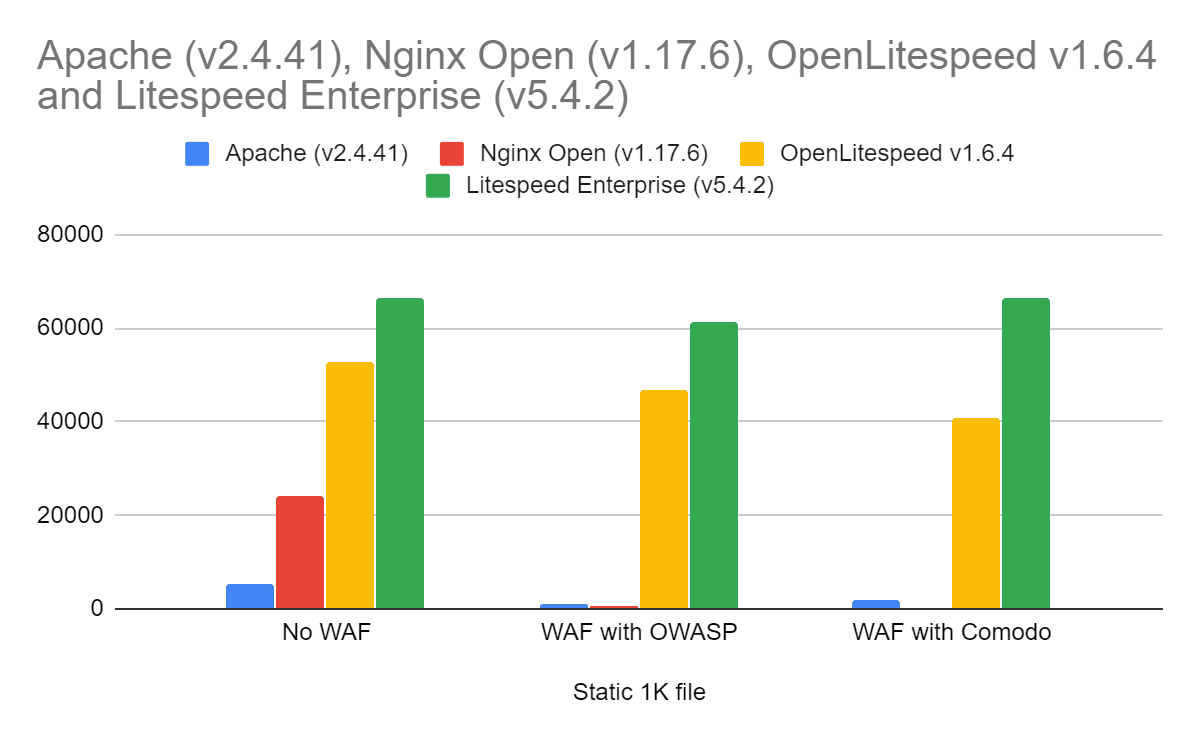
When it comes to serving websites, the choice of a web server plays a crucial role in determining performance, scalability, security, and ease of management. Two popular options that often come up in discussions are Apache HTTP Server and LiteSpeed Web Server. Both are widely used, but they come with different strengths and trade-offs.
In this post, we’ll compare Apache and LiteSpeed across several key factors to help you understand their differences and decide which one best fits your needs.
What is Apache HTTP Server?
Apache HTTP Server, often simply referred to as Apache, is one of the oldest and most widely used open-source web servers in the world. Originally launched in 1995, Apache has stood the test of time due to its flexibility, stability, and robust feature set.
Apache supports various operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and macOS, and is highly customizable thanks to its modular architecture. It also supports a wide range of protocols, such as HTTP/1.x, HTTP/2, and can be extended with various modules to provide additional features like URL rewriting, caching, SSL support, and more.
Pros of Apache:
Open Source: Apache is free to use and backed by a large community, making it highly customizable and well-documented.
Flexibility: Its modular system allows you to add or remove features based on your needs.
Mature Ecosystem: With over two decades of development, Apache has a mature and stable ecosystem.
Compatibility: Apache works well with a variety of programming languages (PHP, Perl, Python, etc.) and databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL).
Cons of Apache:
Performance Under Load: While Apache is highly configurable, its performance can degrade under heavy traffic, especially with a high number of concurrent connections. This is due to its multi-process architecture, where each connection is handled by a separate process, consuming more resources.
Higher Resource Consumption: Apache is known for being resource-heavy, which can impact performance on resource-limited servers.
What is LiteSpeed Web Server?
LiteSpeed Web Server is a commercial, high-performance web server designed to offer faster speeds and better resource management than traditional servers like Apache. LiteSpeed is optimized for serving dynamic content and is known for its ability to handle large amounts of traffic while using fewer resources than Apache.
LiteSpeed comes in two versions: LiteSpeed Open Source (a free version) and LiteSpeed Enterprise (the paid, feature-rich version). While LiteSpeed Open Source has many benefits, the Enterprise version provides additional features, such as improved security, scalability, and the ability to handle heavy traffic loads with enhanced caching mechanisms.
Pros of LiteSpeed:
Performance: LiteSpeed is known for its exceptional performance, especially when serving dynamic content like PHP. It uses an event-driven architecture that allows it to handle high traffic more efficiently, consuming fewer system resources than Apache.
Built-in Caching: LiteSpeed comes with LiteSpeed Cache (LSCache), a powerful caching engine that can dramatically speed up websites without requiring additional plugins or configuration.
HTTP/3 Support: LiteSpeed supports the latest web protocols, such as HTTP/3 and QUIC, for faster load times and better performance on mobile networks.
Security: LiteSpeed includes a number of built-in security features, such as anti-DDoS, automatic blocking of malicious requests, and protections against specific attack types (e.g., SQL injection).
Compatibility with Apache: LiteSpeed can serve .htaccess files (Apache’s configuration files) and mod_rewrite rules, making it easy to migrate from Apache without significant changes to your existing setup.
Cons of LiteSpeed:
License Costs: The full-featured Enterprise version of LiteSpeed is not free, which might be a barrier for some users, especially those on a tight budget.
Smaller Community: Compared to Apache, LiteSpeed has a smaller community, meaning there might be fewer community-contributed resources and less support in some cases.
Key Differences Between Apache and LiteSpeed
- Performance and Scalability
Apache: Apache is a process-based server, meaning it spawns a new thread or process for each incoming request. While this provides stability and isolation, it can be resource-intensive and slower under high traffic.
LiteSpeed: LiteSpeed uses an event-driven, asynchronous model, allowing it to handle thousands of concurrent connections without consuming large amounts of memory. This leads to much better performance, particularly on high-traffic websites. - Speed and Efficiency
Apache: Apache is generally slower than LiteSpeed, especially when serving dynamic content like PHP. Apache’s default configuration is not optimized for performance, and additional modules or configurations are often required to boost speed.
LiteSpeed: LiteSpeed is built for speed, offering built-in optimizations for dynamic content. It also integrates seamlessly with caching solutions (such as LSCache), providing instant performance improvements without the need for third-party tools. - Security
Apache: While Apache offers solid security features, its configuration can be complex, and it may require additional modules to secure certain areas of a website (e.g., protection against DDoS attacks, SQL injection, etc.).
LiteSpeed: LiteSpeed comes with more robust security out-of-the-box, offering features like protection against brute force attacks, automatic blocking of malicious bots, and easier configuration of SSL. - Ease of Use
Apache: Apache’s configuration system is highly flexible but can be difficult to manage for beginners. It requires knowledge of configuration files and modules to optimize and secure the server.
LiteSpeed: LiteSpeed is generally easier to configure and manage, especially with its integrated control panel and built-in features like LSCache. For users coming from Apache, LiteSpeed’s compatibility with Apache’s .htaccess files makes migration easier. - Cost
Apache: Apache is completely free and open-source, making it a great option for budget-conscious users or those who want full control over their server environment.
LiteSpeed: LiteSpeed’s Open Source version is free, but many of its advanced features, such as enhanced caching, scalability, and security, are only available in the paid Enterprise version. - Support
Apache: Being one of the most widely used web servers, Apache has a large community and extensive documentation, so finding support or tutorials is relatively easy.
LiteSpeed: LiteSpeed offers premium support, especially for users of the Enterprise version, but its community is smaller compared to Apache.
Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between Apache and LiteSpeed largely depends on your specific needs and budget.
Choose Apache if:
You’re looking for a free, open-source solution with a large community and a flexible feature set.
You need a highly customizable server that supports a wide range of modules and configurations.
Your website’s traffic is relatively low to moderate, and performance is not a critical concern.
Choose LiteSpeed if:
- You need superior performance, especially for dynamic content like PHP-based websites (WordPress, Joomla, etc.).
- You’re dealing with high traffic or need to optimize for speed and scalability.
- You want a web server that comes with built-in caching, security features, and faster load times without relying on third-party plugins.
- You’re willing to invest in a commercial license for additional features and premium support.
In the battle of Apache vs. LiteSpeed, there’s no clear-cut winner for every use case. Apache remains a powerful and flexible option for many webmasters, especially those working with custom configurations or smaller-scale websites. However, for high-performance needs, especially when dealing with large amounts of dynamic content or high traffic, LiteSpeed often comes out on top.
Ultimately, the best choice will depend on your specific requirements, your server environment, and your willingness to invest in a paid solution.